Radiation: Types, Effects, and Safety Measures
March 31, 2024
Science
Radiation is a phenomenon that surrounds us every day, yet its understanding often eludes many. From the sun’s rays to medical X-rays, radiation plays a significant role in various aspects of our lives. However, misconceptions and fears about radiation persist due to its association with nuclear disasters and its invisible nature. In this article, we delve into the world of radiation, exploring its types, effects, and the safety measures in place to mitigate its risks.
Types of Radiation:
Radiation encompasses a broad spectrum of energy emitted in various forms. The primary types of radiation include:
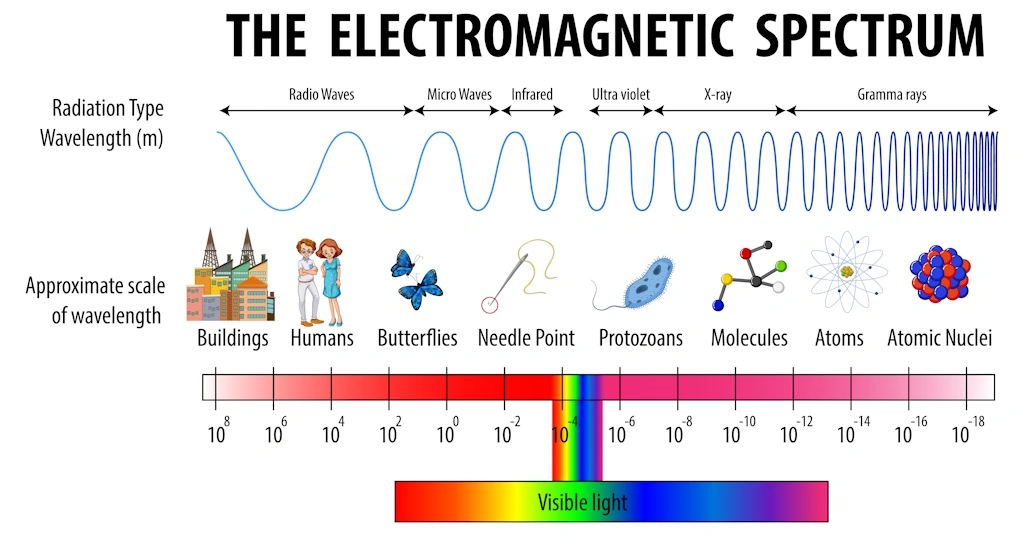
- Electromagnetic Radiation: This form of radiation consists of waves of electric and magnetic fields propagating through space. Examples include visible light, radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays. Electromagnetic radiation differs in wavelength and frequency, with shorter wavelengths carrying higher energy.
- Ionizing Radiation: Ionizing radiation possesses enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, leading to the formation of charged particles or ions. This type of radiation includes X-rays, gamma rays, and cosmic rays. Ionizing radiation is commonly used in medical imaging, cancer therapy, and industrial applications.
- Non-ionizing Radiation: Unlike ionizing radiation, non-ionizing radiation lacks sufficient energy to ionize atoms. Examples include radiofrequency radiation from cell phones, microwaves, and visible light. While non-ionizing radiation is generally considered less harmful, prolonged exposure to certain frequencies may still pose health risks.
Effects of Radiation:
The effects of radiation on living organisms vary depending on factors such as the type of radiation, dose, duration of exposure, and sensitivity of the organism. Here are some of the key effects:
Biological Effects: Ionizing radiation can damage cellular structures, including DNA, leading to mutations, cell death, and potential long-term health effects such as cancer. Acute exposure to high doses of ionizing radiation can cause radiation sickness, characterized by symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
- Health Risks: Prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation increases the risk of developing various health conditions, including cancer, cataracts, and cardiovascular diseases. However, the actual risk depends on factors such as the type of radiation, dose received, and individual susceptibility.
- Environmental Impact: Radiation can also impact the environment, affecting ecosystems and biodiversity. Nuclear accidents, such as the Chernobyl and Fukushima disasters, have resulted in radioactive contamination of soil, water, and wildlife, leading to long-term ecological consequences.
Safety Measures and Regulations:

To mitigate the risks associated with radiation exposure, stringent safety measures and regulations are in place across various industries. These measures aim to protect workers, the public, and the environment from the harmful effects of radiation. Some key safety practices include:
- Radiation Shielding: Using materials such as lead, concrete, and water to attenuate or absorb radiation can reduce exposure levels in workplaces where radiation is present.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers handling radioactive materials or operating radiation-emitting equipment are required to wear appropriate PPE, including lead aprons, gloves, and goggles, to minimize exposure.
- Dose Limits: Regulatory bodies establish dose limits for radiation exposure based on scientific research and risk assessments. These limits ensure that radiation doses received by workers and the public remain below levels considered harmful.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Regular monitoring of radiation levels in workplaces and the environment helps identify potential hazards and ensures compliance with safety standards. Dosimeters worn by workers measure their radiation exposure over time.
- Training and Education: Providing comprehensive training and education to workers on radiation safety practices, emergency procedures, and the potential risks associated with radiation exposure is crucial for maintaining a safe work environment.
Conclusion:
Radiation is a fundamental aspect of our world, with both beneficial applications and potential risks. Understanding the different types of radiation, their effects on health and the environment, and the safety measures in place to minimize risks is essential for effectively managing radiation-related activities. By adhering to strict safety protocols and regulations, we can harness the benefits of radiation while safeguarding human health and the environment.
Note : The provided information may contain errors; please contact us if you notice any.
Image source: Freepik(stockgiu) , Freepik , Freepik(brgfx)

















