Exploring the Revolutionary Frontier of 3D Printing
April 8, 2024
Technology
In the realm of technological innovation, few advancements have captured the imagination quite like 3D printing. From humble beginnings as a niche manufacturing technique to its current status as a transformative force across industries, the journey of 3D printing has been nothing short of remarkable. In this blog, we delve into the fascinating world of 3D printing, exploring its origins, applications, and the boundless possibilities it presents for the future.
The Genesis of 3D Printing:
The roots of 3D printing can be traced back to the 1980s when Chuck Hull, a physicist and engineer, invented stereolithography (SLA), a process that utilized UV light to solidify layers of photopolymer resin to create 3D objects. This breakthrough laid the foundation for additive manufacturing, a technique where objects are built layer by layer from digital designs.
Over the years, advancements in materials, software, and printing technologies have propelled 3D printing into the mainstream. Today, 3D printers can produce an array of objects ranging from prototypes and tools to medical implants and even food.
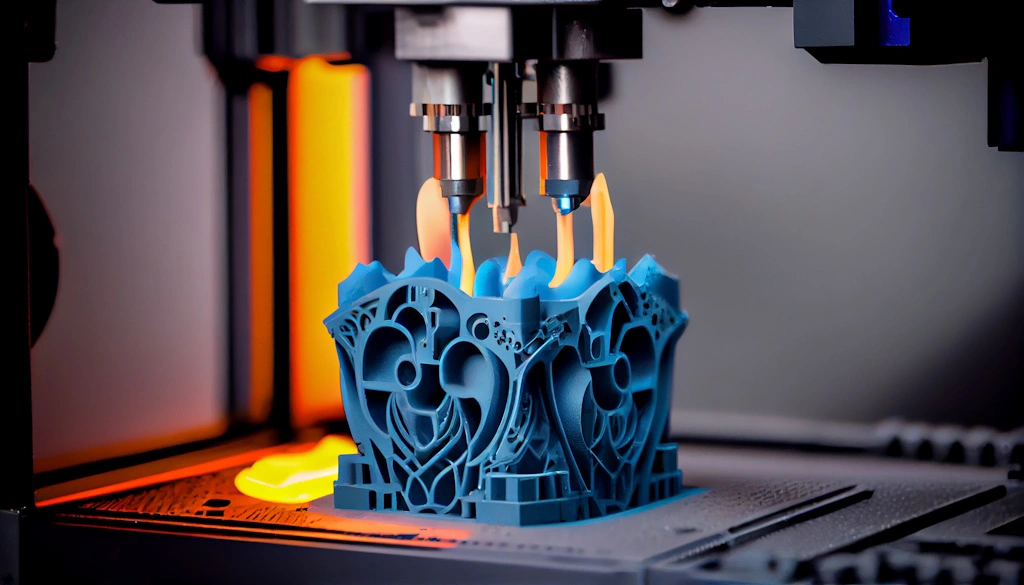

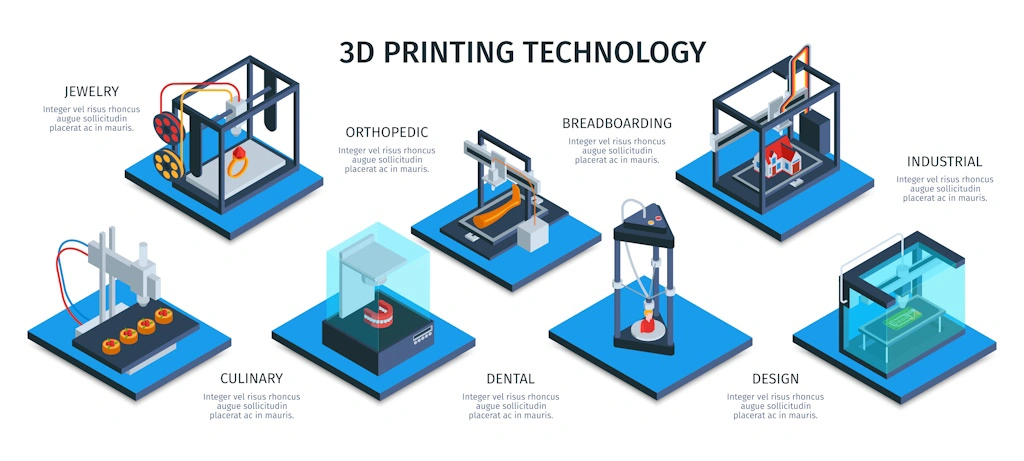
Applications Across Industries:
One of the most compelling aspects of 3D printing is its versatility, which has led to its adoption across various industries:
- Manufacturing: 3D printing has revolutionized traditional manufacturing processes by enabling rapid prototyping, reducing lead times, and facilitating on-demand production. Companies can now iterate designs quickly and efficiently, saving both time and resources.
- Healthcare: In the field of medicine, 3D printing has emerged as a game-changer, facilitating the creation of patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and even organs. From custom-fitted orthopedic implants to intricate surgical models, the healthcare industry has embraced 3D printing to improve patient outcomes and enhance medical care.
- Aerospace and Automotive: Aerospace and automotive manufacturers leverage 3D printing to produce lightweight components, streamline supply chains, and enhance design flexibility. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex geometries that were previously impossible to achieve using traditional methods, leading to innovations in fuel efficiency and performance.
- Education and Research: 3D printing has also found its way into educational institutions, empowering students and researchers to bring their ideas to life in tangible form. From engineering prototypes to scientific models, 3D printers serve as invaluable tools for hands-on learning and experimentation.
Future Prospects:
As technology continues to evolve, the future of 3D printing holds immense promise. Researchers are exploring new materials, such as biodegradable plastics and sustainable alternatives, to make 3D printing more environmentally friendly. Additionally, advancements in multi-material printing and nanoscale printing techniques are opening up new frontiers in precision manufacturing and electronics.
Moreover, the concept of distributed manufacturing, where products are printed on-site or on-demand, could disrupt traditional supply chains and usher in a new era of localized production.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, 3D printing represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing and design. Its ability to democratize production, foster innovation, and address complex challenges across industries underscores its transformative potential. As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly shape the way we create, build, and interact with the world around us, ushering in a new era of possibilities limited only by our imagination.
Note : The provided information may contain errors; please contact us if you notice any.
Image source: Freepik(vecstock) , Freepik(macrovector) , Freepik(vecstock)
Technology
















