Vertical Farming: Revolutionizing Urban Agriculture for a Sustainable Future
March 25, 2024
Science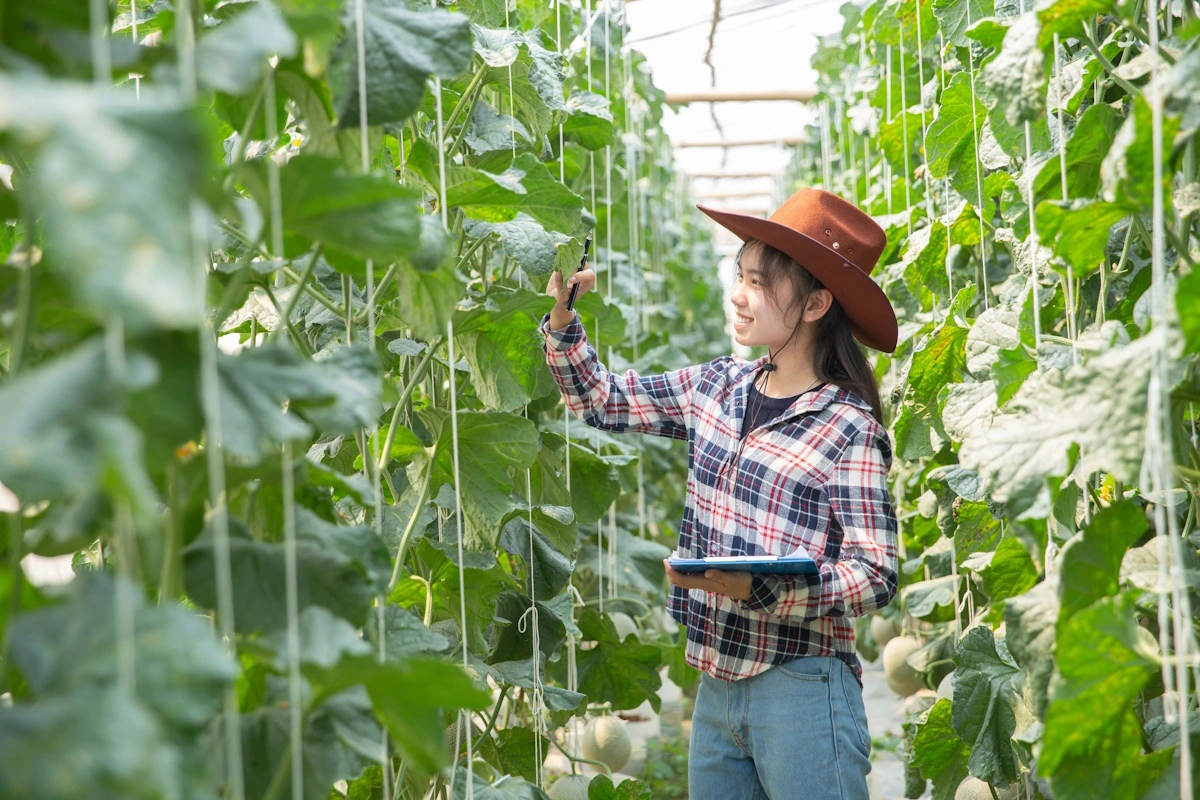
In an era where climate change, population growth, and urban expansion present unparalleled challenges to traditional agriculture, vertical farming emerges as a beacon of innovation and sustainability. This revolutionary farming method, characterized by the cultivation of crops in vertically stacked layers, is not just a testament to human ingenuity but a necessary evolution in how we think about food production in the 21st century.
What Is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming involves growing crops in controlled environments using soilless farming techniques such as hydroponics (growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution), aeroponics (spraying the plant roots with a nutrient solution), and aquaponics (combining fish farming with hydroponics). These methods are integrated into structures such as buildings, shipping containers, and specially designed warehouses, enabling agriculture to thrive in urban settings where traditional farming would be impractical or impossible.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Vertical Farming

Efficient Use of Space and Resources
The spatial efficiency of vertical farming is unparalleled. By growing upwards, these farms significantly reduce the land footprint required for food production, a boon for land-scarce urban areas. The closed-loop systems characteristic of vertical farms recycle water and nutrients, leading to up to 95% less water use than conventional agriculture. Moreover, these controlled environments eliminate the need for harmful pesticides, contributing to healthier, safer food production.
Year-Round Production and Enhanced Crop Yield
Vertical farms operate independently of the external climate, allowing for year-round crop production. This not only boosts food supply reliability but also increases yield; with crops grown in ideal conditions, multiple harvests can be achieved annually, far surpassing the output of traditional farming.
Reducing the Carbon Footprint of Food Production
By situating farms closer to urban consumers, vertical farming slashes the carbon emissions associated with long-haul transportation. This localization of food production also ensures fresher produce, enhancing both nutritional value and taste, a critical aspect often compromised in extended supply chains.
Fostering Urban Resilience and Food Security
As cities grow and climate change renders weather patterns more unpredictable, food security becomes increasingly precarious. Vertical farming offers a solution by producing food within urban centers, reducing dependency on rural agriculture and long-distance transportation. This model not only makes cities more self-sufficient but also more resilient to supply chain disruptions, whether caused by extreme weather events or geopolitical tensions.
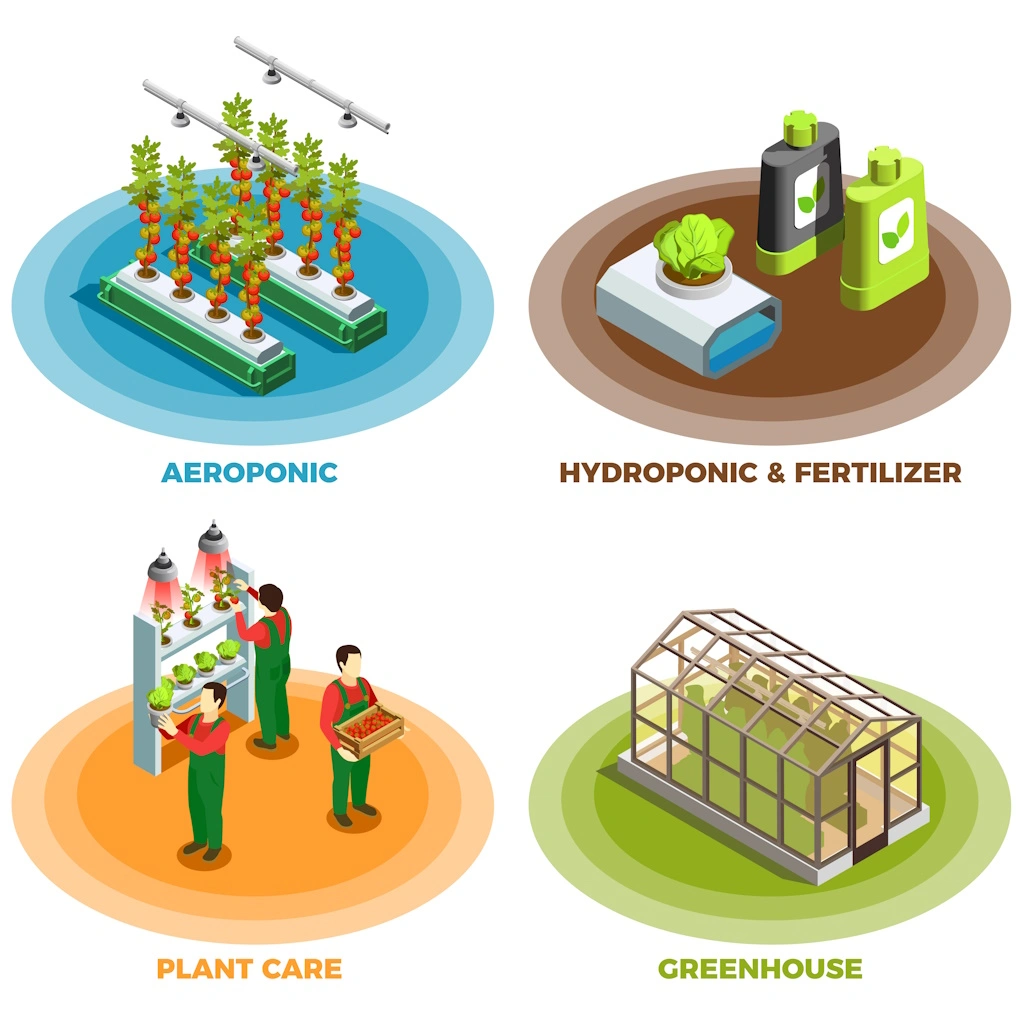
Addressing the Challenges
Despite its potential, vertical farming faces hurdles. High initial capital costs for setup and the ongoing energy expenditure for lighting and climate control are significant barriers. Yet, the rapid advancements in LED lighting efficiency and the increasing viability of renewable energy sources are promising counters to these challenges.
Another concern is the limitation in crop variety. While leafy greens, herbs, and small fruits thrive in vertical farm settings, scaling up to larger crops or those requiring pollination and more space remains a challenge. Ongoing research and technological innovation are crucial to broadening the range of viable crops.
Moreover, there is a pressing need for skilled labor—people who not only understand the intricacies of agriculture but are also adept at managing the sophisticated technology that underpins vertical farms. As such, education and training programs will play a vital role in the sector’s growth.
The Path Forward
The future of vertical farming is inherently linked to advancements in technology and reductions in costs. As renewable energy becomes more accessible and technologies such as AI and machine learning are integrated into farming operations, the efficiency and productivity of vertical farms will continue to improve. These advancements promise not only to make vertical farming more economically viable but also to enhance its sustainability profile.
Collaboration between governments, private sector, and research institutions is critical to fostering innovation and scaling up vertical farming. Policies that encourage urban agriculture, subsidies for sustainable farming practices, and investment in research can accelerate the adoption of vertical farming.
Conclusion
Vertical farming stands at the confluence of necessity and innovation, offering a sustainable path forward for urban agriculture. It presents a compelling solution to some of the most daunting challenges of our time: feeding a growing urban population, conserving resources, and combating climate change. As this farming method evolves, it has the potential to transform not only how we grow food but also how we think about our urban environments and their capability to sustain us. In the journey towards a more sustainable and food-secure future, vertical farming shines as a beacon of hope and innovation.
Note : The provided information may contain errors; please contact us if you notice any.

















